Projects
There is an increasing demand for in vitro models that capture the function of living tissues in the field of medicine and life science. To capture the physiological function in engineered tissues, there is a need to create bio-structures that mimic the hierarchical architecture and complexity of living tissues. By exploiting innovative approaches including microfabrication techniques (MEMS) and material science, we focus on development of three-dimensional engineered tissues for regenerative medicine and fundamental life science.
松永研究室では,細胞・タンパク質・生体高分子などの生体関連要素を,人工的に組み立て・配置することで,高次な三次元組織構造を作製する「ボトムアップ組織工学」に関する研究を進めています.ハイドロゲル形成技術,MEMSなどのマイクロ加工技術,分子細胞生物学等を融合して,生体の疾患部位の微小環境を再現・制御し,疾患の解明,効率的治療へと貢献する基盤技術の創出を目指します.
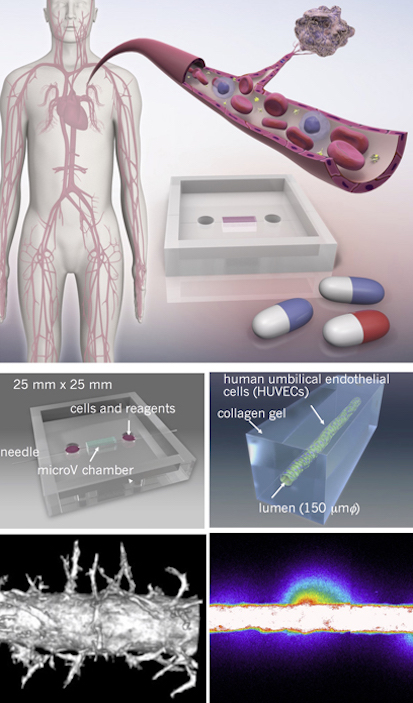
1. Microvessel model
微小血管モデル
Organ-on-a-chip is an innovative platform which incorporates cells of human origin. It can be used to fill the gap between non-clinical studies and clinical studies in drug development. This platform enables recreation of the dynamic and complex microenvironment and the structure of the tissue and hence will be useful for understanding human responses. Our lab aims to visualize disease mechanisms using microvessel model. This model allows us to take control of the spatial arrangement of the cells and other physical and biochemical factors. Microvessels respond in the manner of sprout formation or alteration in the barrier function depending on the added biochemical factors. We combine creation and visualization of the tissue to elucidate what is happening in our bodies.
ヒト培養細胞を用いた医薬品の有効性・安全性試験を可能とする新規評価系が求められており,この解決方法として近年注目されているのがorgan-on-a-chipとよばれるin vitro組織モデルです。その名のとおり,微小な臓器や組織がスライドグラスなどのチップ上に集積されたものを指し,マイクロ加工技術により,複雑で動的な生体の微小環境、構造および機能を再現する試みがなされています.コラーゲンゲルとマイクロ加工技術を用いた三次元微小血管構造形成により,血管新生と血管透過性の双方を評価しうる手法を開発しました。生体外モデルの利点は,その疾患現象に関わる細胞や物理的・化学的因子を任意に配置・変化させ,生体の中でのブラックボックスを細胞レベルで可視化できる点です.腫瘍組織内に血管組織が形成される様子,腫瘍細胞がその血管内へ浸潤する様子など,モデル組織の構築とイメージングを組み合わせ,生体内で起こっている現象を明らかにし,薬剤評価、効果的な治療法の確立,および疾患予防へと役立てることを目標としています.
Press release
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2018/01/180130090832.htm
https://www.iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp/ja/news/2852/
https://www.iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp/ja/news/2655/
E. Lee et al., J. Mater. Chem. B, 6, 1085 (2018)
J. Pauty et al, EBioMedicine, 27, 225-236 (2018)
H. Takahashi et al, Scientific Reports, 7, 42426 (2017)
J. Pauty & R. Usuba et al, Nanotheranostics, 1(1), 103-113 (2017)
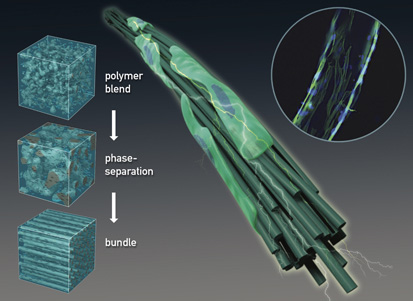
2. Biomaterials as cell scaffold
細胞足場材料としてのバイオマテリアル
Bundles of thin and multiply parallel fibers are widely seen in nature such as plant xylems, human protein assemblies and muscle/nerve tissues. Because of their hierarchical structure, they have superior toughness and strength relative to single fibers, and have been a key research focus in artificial tissue engineering. We have developed a new method to prepare biomimetic bundle-structured gel fibers using a microfluidic device and rapid cross-linking of a phase-separated polymer blend solution. The bundled gels have a feature of tunable surface topology and mechanical stiffness, and allow guiding cell orientation. These properties can be applicable for the cell culture scaffold, especially for muscle/nerve tissue regeneration.
細い繊維が数多くより合わさった束状の構造体は,動植物の体内など自然界で多く見られます.細い繊維が束になった階層構造により,強度や柔軟性に優れたマテリアルを得ることができるため,組織工学分野での利用が期待されています.我々は,セルロースとアルギン酸の混合溶液がネットワーク状の液-液相分離を示す条件を発見しました.これを,マイクロ流体デバイスでの高速架橋を組み合わせることで,束状構造を持つゲルを簡便に作製する技術を開発しました.この束状構造ゲルは,その表面構造や機械的特性を自由に変化させ,表面に接着する細胞の配向性や機能を制御することが可能であり,筋肉や神経の組織再生足場材料への利用が期待できます.
Press release
S. Tachizawa, H. Takahashi et al, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 9(49), 43250-43257(2017)
Y.J. Kim et al, Biomaterials Science, 4, 1197-1201 (2016)
Y.J. Kim & Y. Takahashi et al, J. Mater. Chem. B, 3, 8154-8161 (2015).
3. Vascular Health
血管の健康
It is important to keep blood vessel (capillaries) young in keeping the body healthy. Not only blood vessels are associated with transporting nutrients and oxygen but also they are involved in diseases. We investigate how healthiness of capillaries can be maintained by controlling food intake, exercise and environment.
私たちのからだは隅々まで血管で張り巡らされております.血管は組織に,酸素・栄養分を供給するだけでなく疾患とも密接な関係があります.血管は健康のバロメーター.食・運動・環境を通じ,毛細血管力維持に関する研究を展開しています.

4. Science x Design
科学 x デザイン
"Science for everyone!". In order to connect people and people through science, we conduct various expression activities through design. Our lab members have an opportunity to participate in the projects in RCA x IIS Tokyo Design lab.
科学を通じて人と人とがつながれるよう,デザインを通じたさまざまな表現活動を行っています.希望する研究室メンバーには,所内のRCA x IIS Tokyo Design labでのプロジェクトに参加していただいております.

5. International collaboration
国際連携
Our laboratory is a member of LIMMS, an international collaborative laboratory of CNRS and IIS. In 2014,SMMIL-E which is a new platform for the research on BioMEMS in Lille, France, has started. From April 2022, Matsunaga acts as a Scientific Director.
当研究室はフランス国立科学研究センター(CNRS)と東京大学生産技術研究所(IIS)の国際共同研究ラボLIMMSのメンバーです. 2014年よりLIMMS在仏拠点(SMMIL-E)の活動がはじまりました. 2022年4月より松永がScientific Directorをつとめます.
LIMMS/CNRS-IIS (English)
LIMMS/CNRS-IIS (Japanese)
SMMIL-E
naturejobs.com "Spotlight on Technology Universities in Japan"